Enhanced TDS
Identification & Functionality
- Chemical Family
- Chemical Name
- Base Chemicals Functions
- Cleaning Ingredients Functions
- Cosmetic Ingredients Functions
- Pharma & Nutraceuticals Functions
- CAS No.
- 108-95-2
- EC No.
- 203-632-7
- Technologies
- Product Families
Features & Benefits
- Benefit Claims
- Labeling Claims
Applications & Uses
- Markets
- Applications
- Application Format
- Base Chemicals End Uses
- Skin Care Applications
- End Uses
Phenol is used as a basic feedstock for producing numerous derivatives. The major derivatives and uses are described briefly below.
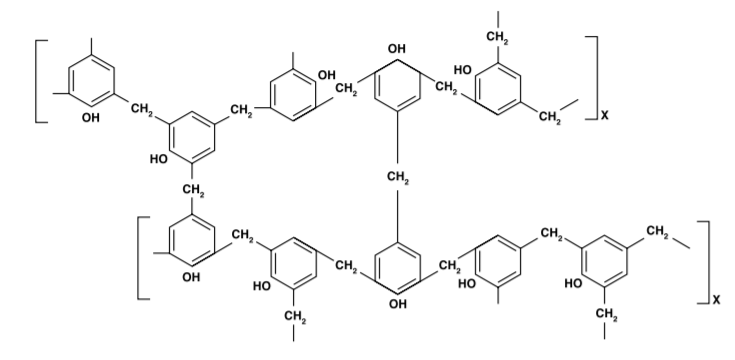
Phenolic Resins
Phenolic resins are the condensation product of phenol or substituted phenols with an aldehyde, such as formaldehyde. The largest use for phenolic resins is in adhesives (for plywood), followed by binders for insulation (fiberglass, mineral wool, etc.), impregnating and laminating agents (for plastic and wood laminates) and molding compounds and foundry resins.
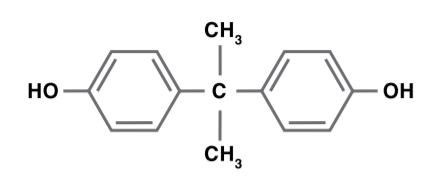
Bisphenol A
Bisphenol A (BPA) is produced by reacting phenol with acetone in the presence of an acid catalyst. There are two major uses for bisphenol A: epoxy resins and polycarbonate resins. Small amounts of bisphenol A are used to produce phenoxy resins, polysulfone resins, polyester resins, adhesives and stabilizers.
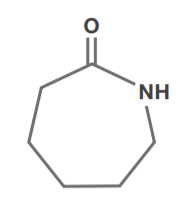
Caprolactam
Caprolactam is produced by hydrogenating phenol with a palladium catalyst to cyclohexanone, and then reacting with hydroxylamine sulfate to produce cyclohexanone oxime. The oxime is then reacted with sulfuric acid and neutralized with aqueous ammonia to produce caprolactam. Caprolactam is polymerized to nylon 6, a polyamide polymer used for fibers, films and engineering plastics.
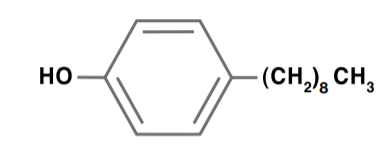
Nonylphenol
Nonylphenol is produced by adding phenol to a branched nonene isomer, or straight-chain nonene, in the presence of an acid catalyst, such as sulfuric acid or boron trifluoride, to produce mostly 4-substituted nonlyphenol. Nonylphenol is used as a surface-active agent, emulsifier, antioxidant and lube oil additive.
Dodeclyphenol
Dodeclyphenol is produced like nonylphenol: phenol is reacted with branched chain dodecenes, in the presence of an acid catalyst, to produce mostly 4-alkylphenol isomers. Dodeclyphenol is used primarily in detergents, lube oil additives and surface-active agents.
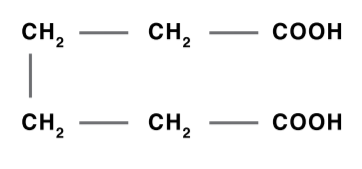
Adipic Acid
Adipic acid is produced by hydrogenating phenol to cyclohexanol, which is then oxidized with nitric acid to adipic acid. Adipic acid is used to produce plasticizers, polyester polyol-based urethane resins, food additives and synthetic lubricants.
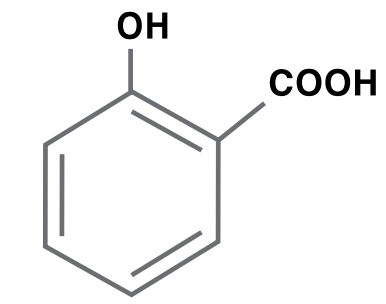
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is produced by reacting phenol with sodium hydroxide to produce sodium phenate, which is reacted with carbon dioxide to produce sodium salicylate and then acidified with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid to form salicylic acid. Salicylic acid is used primarily for drugs and drug intermediates, specialty chemical intermediates, dyes and additives for resins, plastics and rubbers.
Specialized Uses
Phenol is also found in numerous, small-volume applications, including:
- Plasticizers (fire-retardant esters such as cresyl diphenyl, triphenyl, dibutyl phenyl and diphenyl octyl phosphates)
- Synthetic cresols and xylenols (o-cresol and 2, 6-xylenol, which are used for plastics and resins)
- Other alkylphenols (such as p-t-butyl phenol, p-t-octyl phenol and isopropylphenols, which have numerous applications such as surfactant esters)
- Herbicides (2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid)
- Wood preservative (pentachlorophenol)
- Aniline
- Pharmaceuticals
- Dyes
Properties
- Physical Form
- Odor
- Characteristically sweet
- Typical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Color (Molten) max. 20 APHA D-1686-96 (2003)el Purity min. 99.6 wt% D-6142 Solidification Point min. 40.6 °C D-1493-97 Water Content (at loading) max. 0.03 % D-1631-99 Water Content (at receipt) max. 0.1 % D-1631-99 - Physico-Chemical Properties
Value Units Test Method / Conditions Autoignition Temperature 715 (1319) °C (°F) - Boiling Point (760 mmHg) 181.8 (359.2) °C (°F) - Flammable Limits (Lower limit) approx. 1.5 % - Flash Point 79 (174.2) °C (°F) Closed Cup Flash Point 85 (185) °C (°F) Open Cup Freezing Point 40.9 (105.6) °C (°F) - Hygroscopic Yes - - Light Sensitive Yes - - Molecular Weight 94.11 - - Reactivity Stable - - Specific Gravity of Liquid (at 41°C (105.8°F)) 1.058 - - Specific Gravity of Liquid (at 50°C (122°F)) 1.049 - - Specific Gravity of Liquid (at 60°C (140°F)) 1.041 - - Specific Gravity of Solid (at 25°C (77°F)) 1.132 - - Threshold (odor) 0.3 ppm - Threshold Limit Value (8 hours) 5 ppm - Vapor Density (Air = 1.0) 3.24 - - Viscosity of Liquid (at 45°C (113°F)) 3.8 cSt - Viscosity of Liquid (at 60°C (140°F)) 2.52 cSt - Viscosity of Liquid (at 80°C (176°F)) 1.597 cSt - Water Solubility (miscibility at 25°C (77°F)) 9.5 wt% - Weight per gallon (at 50°C (122°F)) 8.75 lb -
Regulatory & Compliance
- Certifications & Compliance
- Grade
Packaging & Availability
- Packaging Type
Storage & Handling
- Storage & Handling
Shipped in water solutions to eliminate molten storage.
For Handling Information Click here
